Credits
16
Prerequisites
Relevant previous coursework
Language of Study
Malagasy, French
Courses taught in
English
Dates
Feb 2 – May 17
Program Countries
Madagascar
Program Base
Antananarivo
Critical Global Issue of Study
Climate & Environment
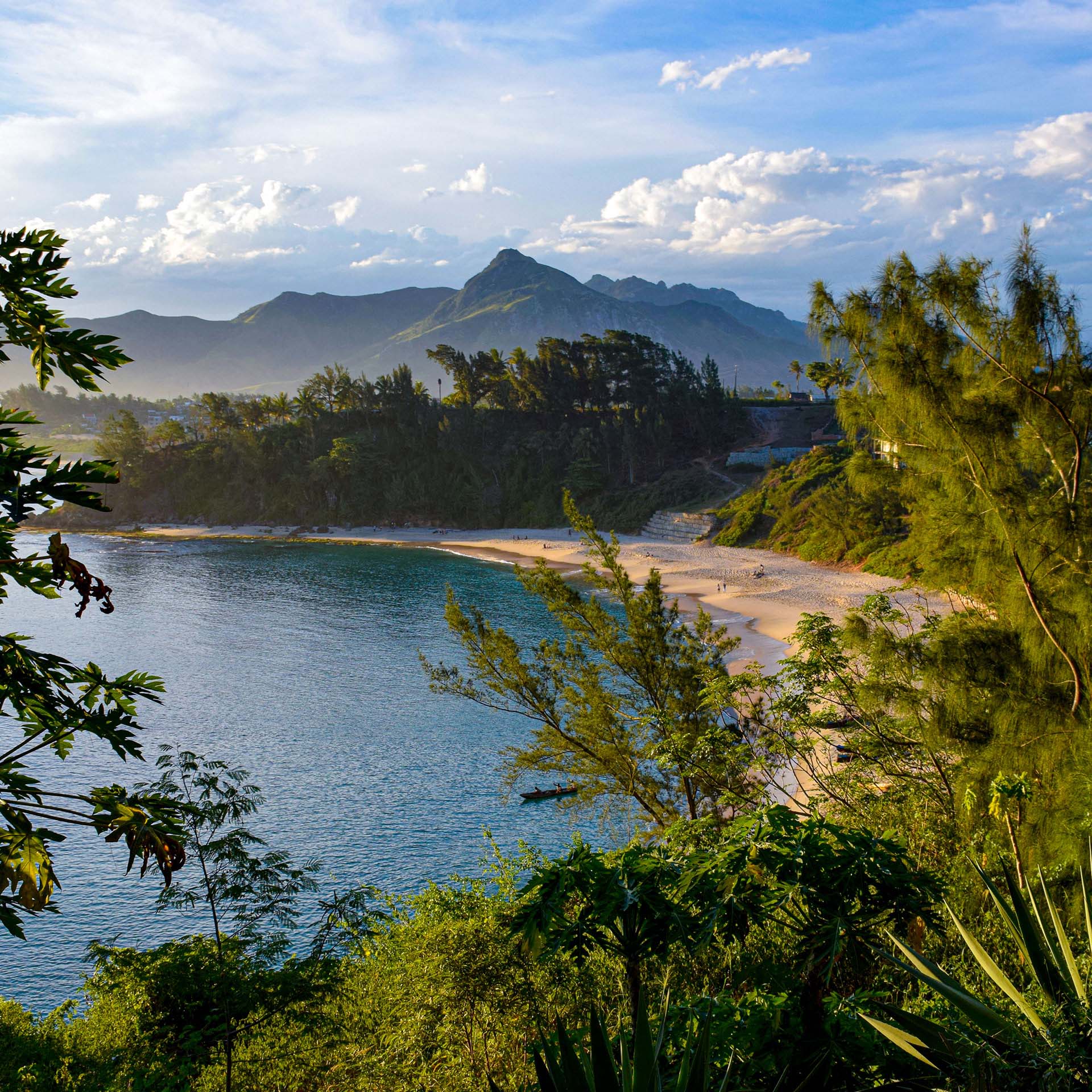

Explore rainforests, mangroves, coral reefs, and the environmental challenges of Madagascar, isolated from neighboring land masses for more than 100 million years.
16
Relevant previous coursework
Malagasy, French
English
Feb 2 – May 17
Madagascar
Antananarivo
Climate & Environment
A biodiverse island evolving from a set of unique environmental circumstances, Madagascar is one of the world’s globally recognized “megadiverse” countries, with flora and fauna found nowhere else on earth. Explore environmental challenges, conservation, and development across an array of ecosystems including tropical rainforests, mangroves, and dry deciduous forests in multiple economic and cultural contexts. Discover a world apart, where the vast majority of wildlife is endemic only to the island and witness the human side of natural resource management. Study alongside Malagasy university students, employing social and natural science field techniques in coral reef systems, national parks, and farming and fishing villages. Stay with local families, and study Malagasy or French. Visit the Ankanin’ny Nofy Reserve, where you can see the iconic aye aye and the carnivorous plant Nepenthes. See the amazing Sarodrano cave, a basin filled with crystal blue fresh water, as well as the beautiful canyon of Isalo National Park.
Previous college-level coursework in environmental studies, ecology, biology, or related fields.
Your semester is based in Antananarivo, where you will hear speakers from the University of Antananarivo and visit the Queens Palace (Rova), Tsimbazaza Botanical and Zoological Park to begin your initiation into Malagasy biodiversity and cultures.
The Maromizaha reserve contains a mix of medium-altitude moist evergreen forest and secondary vegetation, particularly prominent in the northern outskirts of the reserve. Its central area is rich with diverse flora including vines, mosses, lichens, orchids, palms, pandanus, tree ferns, and dragon trees. The dense canopy results in a sparse understory, allowing visitors to observe unique buttress and stilt roots characteristic of plants adapted to humid environments.
The Andasibe habitat is home to a vast number of species, many of them rare and endangered. Among the 11 lemur species is the Indri, the largest of the lemurs. Visit the Amphibian Breeding Center, Mantadia National Park, and two community-based conservation reserves. Akanin’ny Nofy Reserve is a picturesque location on the east coast of Madagascar where you can see the iconic Aye-aye lemur as well as the carnivorous Nepenthese plant.
Your marine study will take place at Tulear, followed by excursions to southern Madagascar to see the rich biodiversity of this part of the island. Visit the Sarodrano cave; Foniala spiny forest and Isalo National Park.
Please note that SIT will make every effort to maintain its programs as described. To respond to emergent situations, however, SIT may have to change or cancel programs.
Upon successful completion of the program, students will be able to:
The following syllabi are representative of this program. Because courses develop and change over time to take advantage of dynamic learning opportunities, actual course content will vary from term to term.
The syllabi can be useful for students, faculty, and study abroad offices in assessing credit transfer. Read more about credit transfer.
Biodiversity and Conservation – syllabus
(ENVI3000/ 3 credits)
Biodiversity in Madagascar is closely linked to the well-being of local communities and the availability of natural resources. However, competition for these resources is increasing due to climate change, drought, poverty, habitat loss, and human development. Also, given practical constraints, conserving all aspects of biodiversity and natural features is not feasible. Our seminar on the conservation of biodiversity will introduce students to the science of biodiversity and to the ecological underpinnings of species extinction and conservation. This background will provide an understanding of methods for protecting and enhancing biodiversity, particularly the use of protected areas.
Natural Resource Management Seminar – syllabus
(ENVI3005 / 3 credits)
This interdisciplinary course introduces students to a range of key policies and practices for the management of the unique and endemic natural resources in Madagascar. Using conceptual approaches drawn from environmental justice and political ecology, students explore diverse terrestrial and marine resources in a range of locales and consider the realities and challenges of developing effective and equitable natural resource management systems. Key themes through which the issues are explored during the course include livelihoods and stakeholder analyses, protected area and community-based management systems and the cultural practices and their influence on natural resource management.
Malagasy – syllabus
Malagasy (French version) – syllabus
(MALA1003 / 3 credits)
Emphasis on beginning speaking and comprehension skills through classroom and field instruction. Formal instruction is augmented by language practice with homestay families.
OR
Beginner students with some prior French knowledge are placed into the appropriate language course level (FREN 1003 or FREN 1503) based on oral proficiency interviews conducted during orientation in Antananarivo.
(FREN1003 and FREN1503 / 3 credits)
This intensive course is intended for students who have little or no prior experience with the French language and are preparing to use it effectively in everyday situations in Madagascar. The main goal of the course is to help students engage with the local Malagasy culture, especially during their urban homestay. Therefore, the course primarily focuses on developing speaking and listening skills, with reading and writing as secondary components to support verbal communication and comprehension. Throughout the course, students will also be exposed to the cultural context through audiovisual materials and text book that will cover pronunciation, basic grammar, vocabulary, and sentence structure. The course covers all four key communication skills: speaking, listening, reading, and writing, which will be taught through traditional classroom lessons, field activities, and continuous practice during the homestay experience.
French for Natural Sciences – syllabus
(FREN2003-2503 / 3 credits)
French for Natural Sciences – syllabus
(FREN3003-3503 / 3 credits)
Focusing on oral proficiency in the context of the natural sciences with a biodiversity and natural resource management concentration, language teaching is targeted toward the many activities in the thematic and research methods seminars in order to help students work more independently in the field. The objective is to facilitate students’ interactions with a range of professionals in the field working to manage resources while promoting development within the local cultural context. In support of these objectives, course content provides additional focus on fundamentals of spoken and written French to increase student capacity. Based on in-country evaluation, including oral proficiency testing, students are placed in the appropriate level, with additional language practice in homestays and on field visits.
Environmental Research Methods and Ethics – syllabus
(ENVI3500 / 3 credits)
Conducted primarily in English, this is a course in social and natural sciences research methods. The focus is on learning how to collect, analyze, integrate, and report social and ecological data to critically understand and evaluate various environmental issues. The course serves as an introduction to the Independent Study Project and includes a focus on field study ethics and the World Learning/SIT Human Subjects Review Policy. Field studies may include designing a research project; writing a proposal; interviewing; surveys; and maintaining a field journal. Specific ecological field study methods may include habitat surveys; biotic sampling and analysis; fauna and flora identification; biodiversity monitoring; population censusing; and animal behavior.
In addition to taking the above courses, students will also need to enroll in one of the following two courses:
Independent Study Project
Independent Study Project – syllabus
(ISPR3000 / 4 credits)
Conducted primarily in northern Madagascar or other appropriate locations. Sample topic areas: reforestation; coral reef conservation; medicinal plants in the marketplace; ecotourism; carbon sequestration and financing; land tenure reform and agricultural production; conservation assessments of endangered species; cash crop production and links to local livelihoods; sacred forests; community-based resource management; behavioral ecology of lemurs; sustainable land use techniques.
Sample ISP topic areas:
Browse this program’s Independent Study Projects / undergraduate research.
OR
Internship and Seminar
Internship and Seminar – syllabus
(ITRN3000 / 4 credits)
You will gain valuable work experience and enhance your professional skillset in an international work environment, drawing on the wide network of community organizations, activists, entrepreneurs, business leaders, and academics connected to the program.
Sample internships:


Recent positions held by alumni of this program include:
Director of international programs and global health fellowships at Norfolk Academy, Norfolk, VA
Executive director of EduFood, Oxford, MS
National Science Foundation fellow and PhD candidate in Virginia Tech’s Department of Fish and Wildlife Conservation, Blacksburg, VA
Assistant professor of environmental studies at Middlebury College, Middlebury, VT
Chief of party for USAID forest land tenure programs in Africa
Alumni are also working in climate change and sustainable development, renewable energy, sustainable living design, permaculture, business development and strategic growth, medicine, and law.


SIT Study Abroad is committed to ensuring that international education is within reach for all students. We believe in the transformative power of immersive, intercultural experiences and are dedicated to supporting students in their educational journey.
See Full Breakdown
A critical step in preparing for your study abroad program is planning how you will maintain your health and wellbeing. Please review the following information carefully and contact [email protected] with any questions or concerns.
View Information