Credits
16
Prerequisites
None
Courses taught in
English
Dates
Aug 31 – Dec 13
Program Countries
Italy, Netherlands, United Kingdom
Program Base
Netherlands, United Kingdom, Italy
Visa
Varies
Critical Global Issue of Study
Development & Inequality
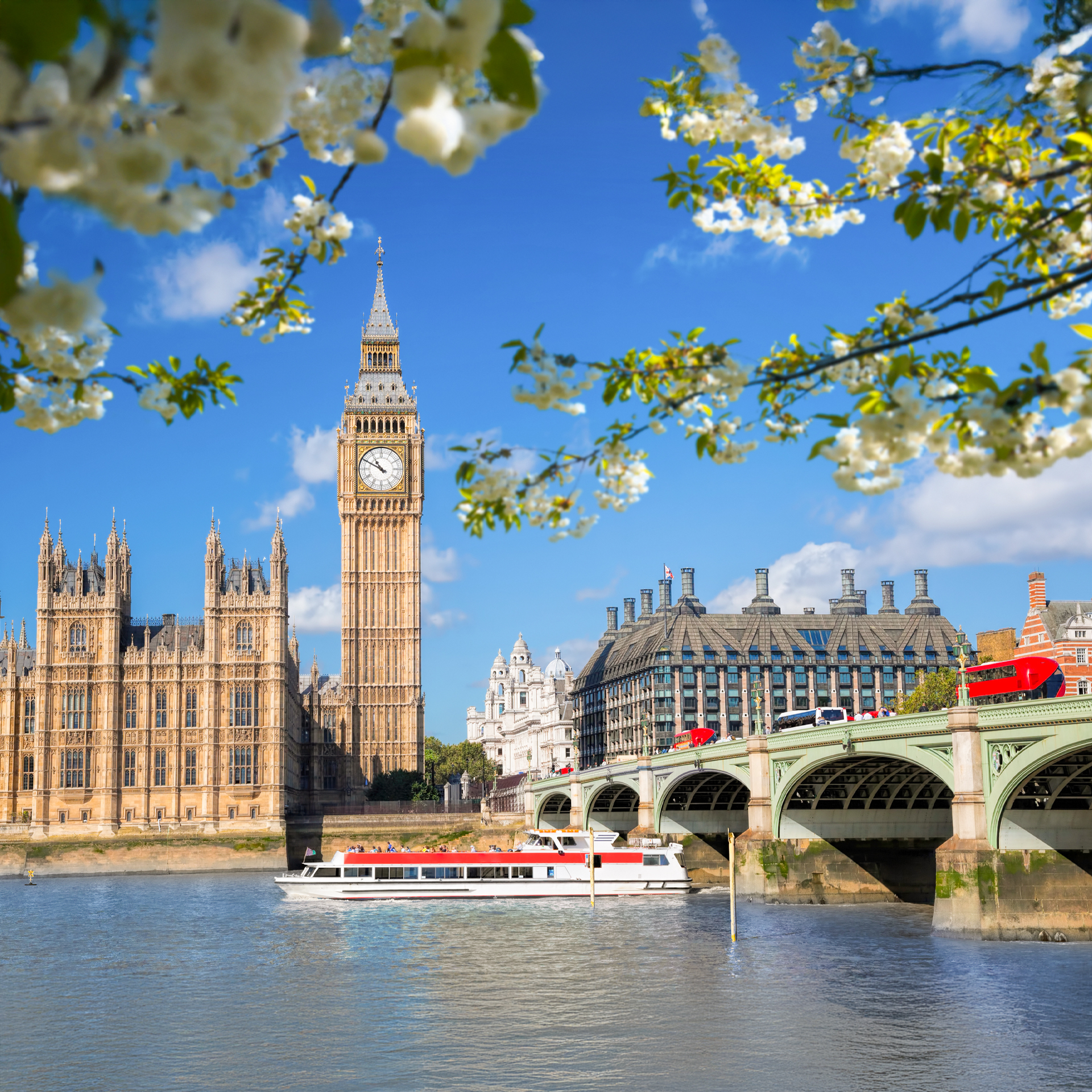

Urban Europe: Explore cities, understand urban challenges—what shapes them, what threatens them, what’s next.
16
None
English
Aug 31 – Dec 13
Italy, Netherlands, United Kingdom
Netherlands, United Kingdom, Italy
Varies
Development & Inequality
This program offers a unique, hands-on exploration of three vibrant European cities, diving into their design, culture, and the challenges they face today. Students will compare how history, politics, culture, and environmental issues have shaped each city, and how these urban centers influence the broader European landscape.
Key topics include public infrastructure, affordable housing, sustainability, and preserving cultural heritage while adapting to change. The program also explores current issues like aging infrastructure, rising inequality, and housing shortages, alongside challenges such as globalization, climate change, and overtourism.
Through immersive experiences, site visits, guided excursions, and conversations with local experts, students will gain real-world insights into the complexities of urban life. They’ll also analyze innovative policy responses and community-driven solutions, helping cities become more sustainable, resilient, and inclusive. By the end, students will walk away with practical skills and knowledge to navigate the evolving dynamics of urban Europe, preparing them for careers in urban development, sustainability, policymaking, and beyond.
Receive up to $1,000 in flight credits when you join this new program! Learn more HERE
None.
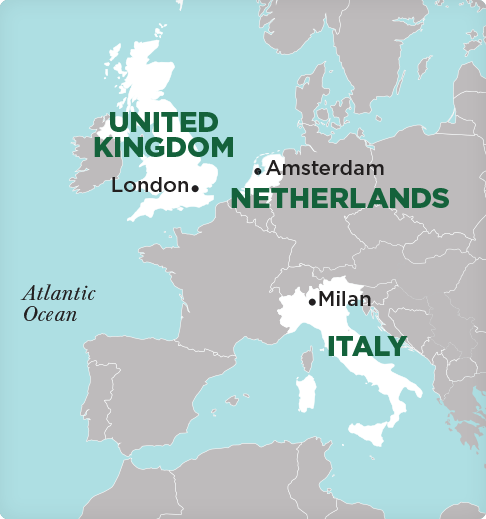
With its complex blend of history, cultural diversity, and cutting-edge urban innovation, Amsterdam offers valuable lessons in urban evolution. The city’s history provides a compelling backdrop for exploring contemporary city life, especially in relation to its ongoing challenges with social integration and inequality. Amsterdam’s efforts to address modern urban issues such as climate change, housing, and overpopulation through sustainable practices like green infrastructure, cycling-friendly design, and Smart City technologies make it a leader in urban innovation. This combination of historical depth, cultural complexity, and forward-thinking sustainability offers students a unique opportunity to study the interplay of past, present, and future challenges in European cities.
London’s rich history as the heart of the British Empire and its industrial transformation offers a context for deep understanding of urban growth. The city’s vibrant, diverse population creates a dynamic mix of idealized images and real-life experiences. London faces challenges like housing inequality, social exclusion, and wealth disparity, while also working to become more sustainable through green spaces, low-carbon transportation, and urban regeneration. These complexities make London an ideal city for exploring how competing city narratives shape urban policies and everyday life.
A city renowned for its fashion, design, and economic innovation, Milan blends cultural vibrancy with cutting-edge urban planning. Its evolution from a Renaissance cultural center to an industrial and economic powerhouse highlights the city’s adaptability and resilience. Despite its prosperity, Milan faces important urban challenges, including affordable housing, gentrification, and the integration of migrants. The city’s efforts to balance economic growth with social inclusion, while fostering sustainability, make it an essential case study in how cities can address both economic development and social cohesion.
Please note that SIT will make every effort to maintain its programs as described. To respond to emergent situations, however, SIT may have to change or cancel programs.
Upon successful completion of the program, students will be able to:
The following syllabi are representative of this program. Because courses develop and change over time to take advantage of dynamic learning opportunities, actual course content will vary from term to term.
The syllabi can be useful for students, faculty, and study abroad offices in assessing credit transfer. Read more about credit transfer.
Urban History of Contemporary Europe – syllabus
(URST-3000 / 4 credits)
This course examines the historical evolution of Amsterdam, London, and Milan, focusing on how each city became a significant urban center shaped by economic, political, and cultural forces. Students will examine Amsterdam’s rise as a trade hub during the Dutch Golden Age, London’s evolution into the heart of the British Empire and its role in industrialization, and Milan’s transformation from a Renaissance center to an industrial powerhouse and global leader in fashion and design. By studying key historical turning points, students will gain a deeper understanding of how cities have adapted to external pressures and reinvented themselves over time. The course highlights how migration, colonialism, war, and globalization shaped the cultural and economic identities of these cities and their impact on European history.
Cities of the Future – syllabus
(IDST-3050 / 4 credits)
This course explores the future of cities in the face of climate change, demographic shifts, affordable housing, and aging infrastructure. Through a comparative study of Amsterdam, London, and Milan, students will examine how these cities are leveraging Smart technology, green infrastructure, and urban planning to address challenges like traffic congestion, pollution, and overpopulation. The course will explore how urban innovation is fostering resilience and sustainability while tackling issues such as inequality and accessibility. Students will analyze the role of cities in adapting to environmental and social stressors, focusing on creating inclusive, livable spaces that support diverse populations and enhance quality of life in an ever-evolving urban landscape.
City Life: Representations and Realities – syllabus
(EURO-3030 / 4 credits)
This course examines how representations of iconic European cities and their cultural institutions popularized across the mediascape perpetuate dominant discourses of inclusion and exclusion in urban life. By contrasting idealized and commercialized narratives with the lived experiences of residents in the center and on the outskirts, students will explore how perceptions of the city and its denizens are constructed and challenged. Special attention will be paid to the role of underground cultural movements and marginalized communities in offering counter narratives. Through field visits, readings, and media analysis, students will contrast competing narratives of the city and its people, exploring how alternative stories challenge mainstream portrayals and reshape the identity of European metropolises.
Project Cities: Community Engagement and Ethical Inquiry – syllabus
(URST-3500 / 4 credits)
This course combines community engagement and self-directed inquiry to deepen students’ understanding of the field of urban studies and the significance of cities. At each program site, students collaborate with local organizations on community-initiated projects while developing intercultural communication and ethical engagement skills. Simultaneously, they pursue an individual, inquiry-based project on a topic related to course themes – such as gentrification, cultural heritage, accessibility, or urban sprawl—through field research and expert interviews. The course culminates in a final integrative project and presentation, fostering a holistic, comparative perspective on global cities.


Potential career paths include:
Urban planner
Cultural heritage manager
Urban policy analyst
Social impact consultant
Urban experience curator
Community development specialist
Sustainability consultant
Smart City technologist
Destination marketing manager
International urban development expert


SIT Study Abroad is committed to ensuring that international education is within reach for all students. We believe in the transformative power of immersive, intercultural experiences and are dedicated to supporting students in their educational journey.
See All Costs
A critical step in preparing for your study abroad program is planning how you will maintain your health and wellbeing. Please review the following information carefully and contact [email protected] with any questions or concerns.

Depending on your passport of origin, you may need a visa for this program. Please contact your admissions officer for more information.